Diseases and Disorders, Urea Cycle Disorders
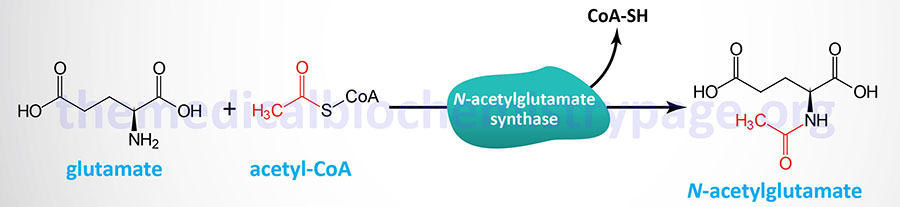
Last Updated: February 13, 2026 Introduction to NAGS Deficiency N-acetylglutamate synthase (deficiency (NAGSD) is most commonly the result of the inheritance of mutations in the NAGS gene which encodes N-acetylglutamate synthase. NAGSD manifests in two forms...

Biochemistry Topics, Nitrogen Metabolism
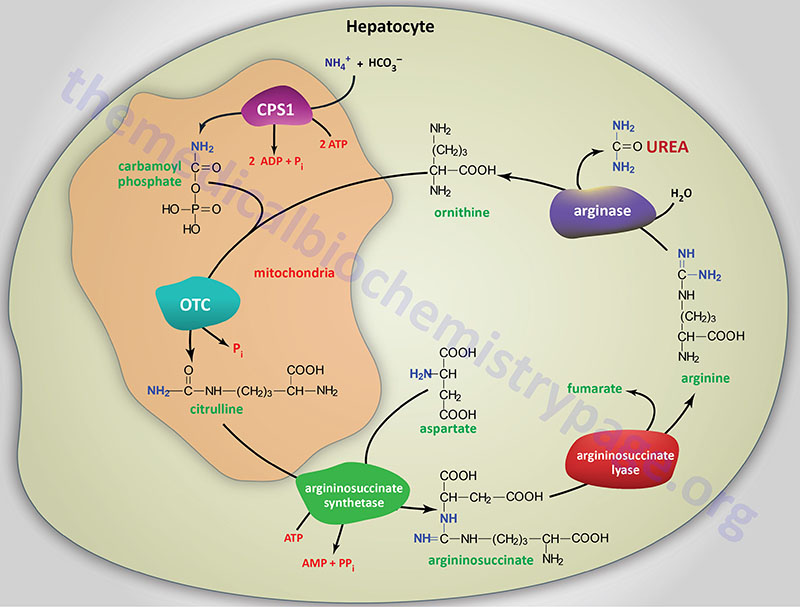
Last Updated: February 13, 2026 Introduction to Nitrogen Homeostasis and the Urea Cycle The processes of nitrogen metabolism, which includes the urea cycle to remove waste nitrogen, are critical to the survival of humans given that excess nitrogen, in the form of...

Diseases and Disorders, Diseases of Amino Acid and Organic Acid Metabolism, Urea Cycle Disorders
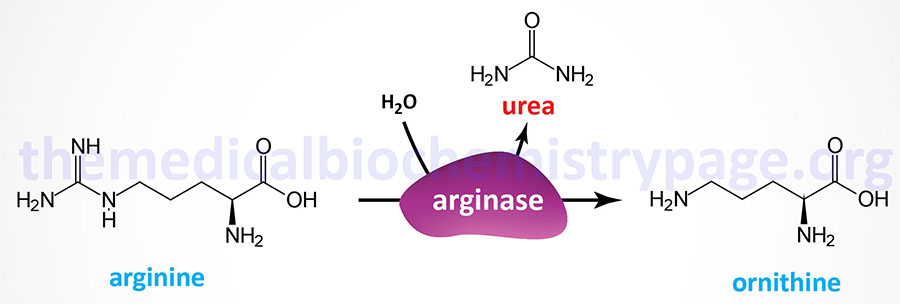
Last Updated: October 28, 2025 Introduction to Arginase Deficiency Arginase deficiency (AD) represents one of the disorders that result from defects in the processes of the urea cycle. Arginase deficiency is a rare autosomal recessive disorder. Arginase deficiency is...

Diseases and Disorders, Diseases of Amino Acid and Organic Acid Metabolism, Urea Cycle Disorders
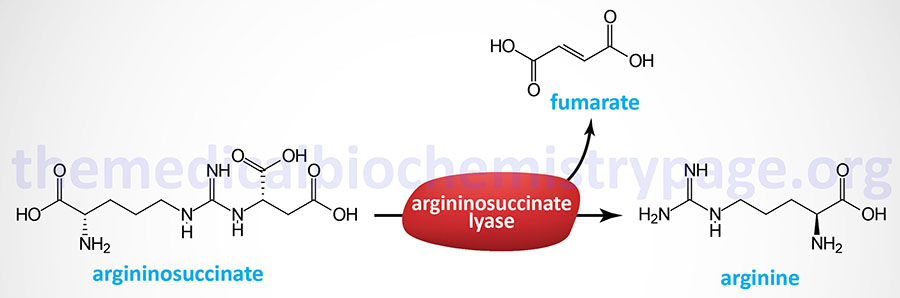
Last Updated: October 30, 2025 Introduction to Argininosuccinate Lyase Deficiency As the name implies, argininosuccinate lyase deficiency (ALD) is a disorder resulting from mutations in the gene (ASL) encoding the urea cycle enzyme, argininosuccinate lyase....

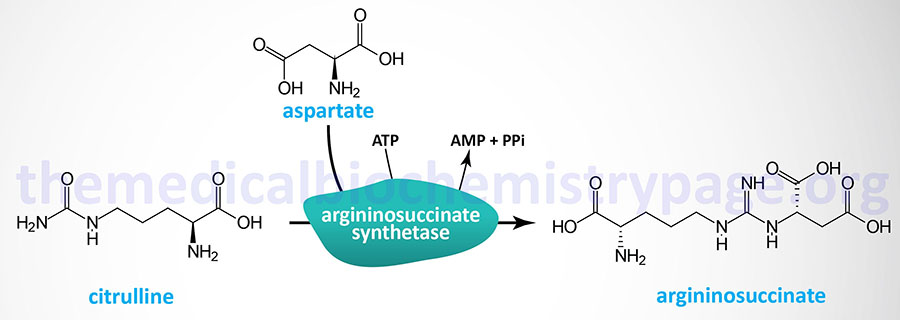
Diseases and Disorders, Diseases of Amino Acid and Organic Acid Metabolism, Urea Cycle Disorders
Last Updated: October 30, 2025 Introduction to Argininosuccinate Synthetase Deficiency Arginosuccinate synthetase deficiency (ASD) is an autosomal recessive disorder of the urea cycle that also affects the synthesis of arginine. This disorder is more commonly referred...