Diseases and Disorders, Diseases of Hormone Synthesis or Function
Last Updated: February 20, 2025 Introduction to Addison Disease Adrenal insufficiency describes a related group of disorders that are generally divided into two broad categories. Disorders that are due to a primary inability of the adrenal glands to synthesize and...

Diseases and Disorders, Diseases of Hormone Synthesis or Function
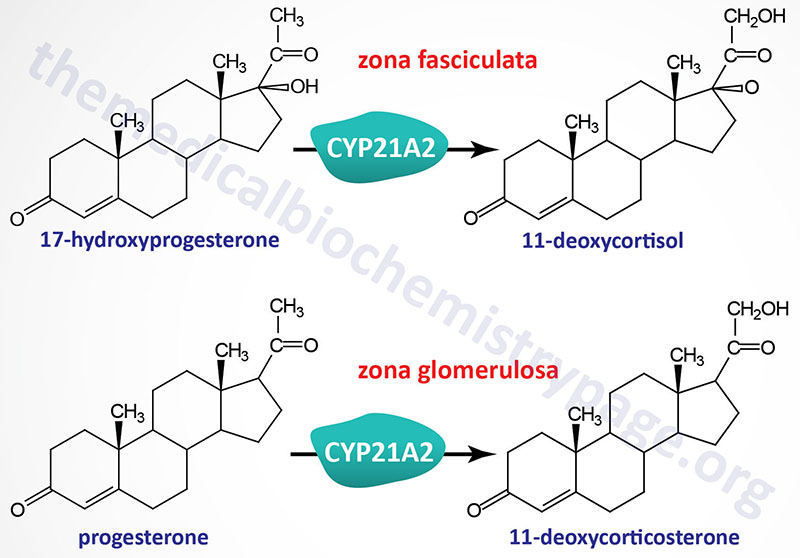
Last Updated: February 20, 2025 Introduction to the Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasias The congenital adrenal hyperplasias (CAH) are a group of inherited disorders that result from mutations in one of several genes involved in adrenal cortical steroid...

Hormones: Steroid & Peptide, Specialized Topics
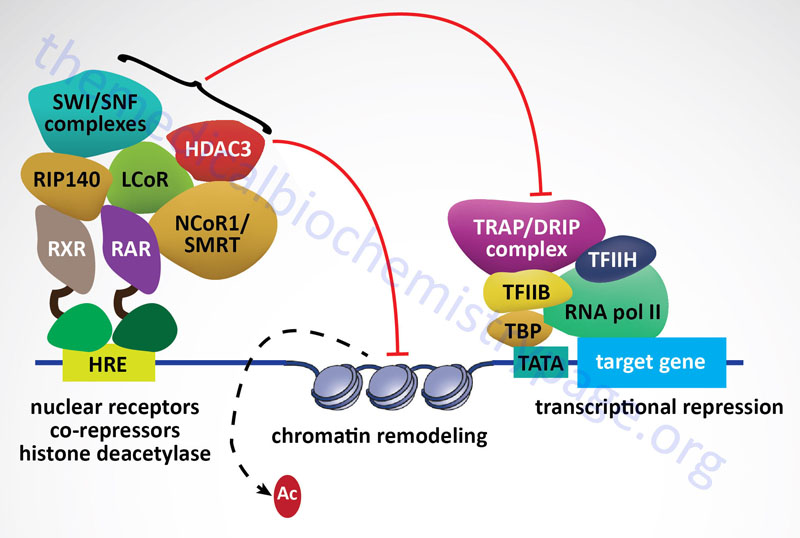
Last Updated: April 1, 2025 Introduction to the Steroid Hormones The steroid hormones are all derived from cholesterol. Moreover, with the exception of vitamin D, they all contain the same cyclopentanophenanthrene ring and atomic numbering system as cholesterol....