Last Updated: March 5, 2026
Introduction to the Lysosomal Storage Disorders
The term “lysosomal storage disorder” (LSD; also referred to as lysosomal storage disease) encompasses a large family of inherited metabolic disorders that are associated with the pathological accumulation of improperly degraded metabolic byproducts within the lysosomes. The consequences of the lysosomal accumulation of undegraded substrates leads to a broad spectrum of clinical manifestations that depends, in part, on the specific substrate as well as the predominant tissue(s) of accumulation. The LSD are associated with a progressive manifestation of symptoms that is variable across the spectrum of LSD, and often is variable within the same characterized disease. The latter is the result of allelic heterogeneity, a term referring to the fact that a number of different mutations in the same gene can result in the same or very similar pathology.
The LSD encompass the mucopolysaccharidotic (MPS) family of diseases that are associated with the abnormal lysosomal accumulation of glycosaminoglycans. The mucolipidoses (e.g I-cell disease; mucolipidosis II) and oligosaccharidoses (e.g. aspartylglucosaminuria) constitute another family of LSD. Pompe disease, which is classically defined as a glycogen storage disease (GSD2) was one of the first diseases characterized as resulting from abnormal lysosomal accumulation of substrate, in this case glycogen. Thus, Pompe disease is both a LSD and a GSD. Another family of LSD include the diseases of sphingolipid metabolism. The neuronal ceroid lipofuscinoses (also referred to as cerebral neurolipofuscinoses) are a group of at least 14 diseases that constitute another family of LSD.
Many of the individual LSD can be classified in more than one subfamily due to the presence of the substrate for an affected enzyme in numerous types of molecules. For instance, sialidosis is classified as an oligosaccharidotic LSD as well as a sphingolipidotic LSD.
Table of the Mucopolysaccharidoses
| Disease: MPS Designation | Enzyme Defect | Gene | Affected GAG | Symptoms / Comments |
| Hurler MPS I, MPS IH (MPS1H) | α-L-iduronidase | IDUA | dermatan sulfate, heparan sulfate | corneal clouding, dysostosis multiplex, organomegaly, heart disease, dwarfism, intellectual impairment; early mortality |
| Scheie MPS I, MPS IS (MPS1S) | α-L-iduronidase | IDUA | dermatan sulfate, heparan sulfate | corneal clouding; aortic valve disease; joint stiffening; normal intelligence and life span |
| Hurler-Scheie MPS I, MPS IHS (MPS1HS) | α-L-iduronidase | IDUA | dermatan sulfate, heparan sulfate | intermediate between I H and I S |
| Hunter MPS II (MPS2) | L-iduronate-2-sulfatase | IDS | dermatan sulfate, heparan sulfate | mild and severe forms, only X-linked MPS, dysostosis multiplex, organomegaly, facial and physical deformities, no corneal clouding, intellectual impairment, death before 15 except in mild form then survival to 20 – 60 |
| Sanfilippo A MPS III, MPS IIIA (MPS3A) | heparan N-sulfatase (also called N-sulfoglucosamine sulfohydrolase | SGSH | heparan sulfate | profound intellectual deterioration, hyperactivity, skin, brain, lungs, heart and skeletal muscle are affected in all 4 types of MPS-III |
| Sanfilippo B MPS III, MPS IIIB (MPS3B) | α-N-acetyl-D-glucosaminidase | NAGLU | heparan sulfate | phenotype similar to III A |
| Sanfilippo C MPS III, MPS IIIC (MPS3C) | acetylCoA:α-glucosaminide-acetyltransferase (also called heparan-α-glucosaminide N-acetyltransferase) | HGSNAT | heparan sulfate | phenotype similar to III A |
| Sanfilippo D MPS III, MPS IIID (MPS3D) | N-acetylglucosamine-6-sulfatase [also called glucosamine (N-acetyl)-6-sulfatase] | GNS | heparan sulfate | phenotype similar to III A |
| Morquio A MPS IV, MPS IVA (MPS4A) | galactose-6-sulfatase (also called [galactosamine (N-acetyl)-6-sulfatase] | GALNS | keratan sulfate, chondroitin 6-sulfate | corneal clouding, odontoid hypoplasia, aortic valve disease, distinctive skeletal abnormalities |
| Morquio B MPS IV, MPS IVB (MPS4B) | β-galactosidase 1 | GLB1 | keratan sulfate | severity of disease similar to IV A |
| MPS V, a designation no longer used | ||||
| Maroteaux-Lamy MPS VI (MPS6) | arylsulfatase B (also called N-acetylgalactosamine-4-sulfatase) | ARSB | dermatan sulfate | 3 distinct forms from mild to severe, aortic valve disease, dysostosis multiplex, normal intelligence, corneal clouding, coarse facial features |
| Sly MPS VII (MPS7) | β-glucuronidase | GUSB | heparan sulfate, dermatan sulfate, chondroitin 4-, 6-sulfates | hepatosplenomegaly, dysostosis multiplex, wide spectrum of severity, hydrops fetalis |
| MPS VIII, a designation no longer used | ||||
| Mucopolysaccharidosis type IX: MPS IX (MPS9) | hyaluronoglucosaminidase-1 (hyaluronidase) | HYAL1 | hyaluronic acids | periarticular soft tissues masses on distal extremities and digits; very rare disease; a total of 36 known pathogenic mutations as of 2025 |
| Mucopolysacchaidosis type X: MPS X (MPS10) | arylsulfatase K | ARSK | dermatan sulfates | metaphyseal striation of the long bones; progressive hip dysplasia; very rare disease with only 10 identified cases as of 2025; a total of 3 known pathogenic mutations as of 2025 |
Table of Oligosaccharidoses and Mucolipidoses
| Disease | Enzyme Deficiency | Gene | Symptoms / Comments |
| Aspartylglucosaminuria | aspartylglucosaminidase (N-aspartyl-β-glucosaminidase) | AGA | progressive intellectual impairment, delayed speech and motor development, coarse facial features |
| I-Cell disease also called mucolipidosis IIA (ML-IIA) or mucolipidosis IIalpha/beta (ML-IIα/β) | UDP-N-acetylglucosamine:lysosomal-enzyme N-acetylglucosaminyl-1-phosphotransferase α- and β-subunits commonly called: GlcNAc-phosphotransferase | GNPTAB | the GNPTAB gene encodes both the α- and β-subunits of the hexameric (α2β2γ2) enzyme; the γ-subunit is encoded by the GNPTG gene; coarse facial features, gingival hypertrophy, recurrent otitis media, cardiac valvular disease; see the I-Cell Disease page for details |
| Pseudo-Hurler polydystrophy also called mucolipidosis III α/β, ML-IIIα/β | UDP-N-acetylglucosamine:lysosomal-enzyme N-acetylglucosaminyl-1-phosphotransferase α- and β-subunits commonly called: GlcNAc-phosphotransferase | GNPTAB | the GNPTAB gene encodes both the α- and β-subunits of the hexameric (α2β2γ2) enzyme; the γ-subunit is encoded by the GNPTG gene; less severe than I-cell disease; short stature, dysostosis multiplex, joint contractures, thickened skin; see the Pseudo-Hurler polydystrophy page for details |
| α-Mannosidosis | α-mannosidase | MAN2B1 | three forms based on age of onset, speed of progression and the overall pathology: type I, type II, and type III; the defective α-mannosidase associated with this disease is encoded by the mannosidase alpha class 2B, member 1 gene (MAN2B1); symptoms include intellectual impairment, dystosis multiplex, hepatosplenomegaly, hearing loss, delayed speech; see the α-Mannosidosis page for details |
| β-Mannosidosis | β-mannosidase | MANBA | the defective β-mannosidase associated with this disease is encoded by the mannosidase beta gene (MANBA); primarily neurological defects, speech impairment, angiokeratoma, hypotonia, behavioral disturbances |
| Galactosialidosis | cathepsin A | CTSA | also identified Goldberg syndrome; disorder can also be the result of a secondary deficiency in β-galactosidase and neuraminidase-1; three distinct subtypes: early infantile, late infantile, and juvenile or adult; see the Galactosialidosis page for details |
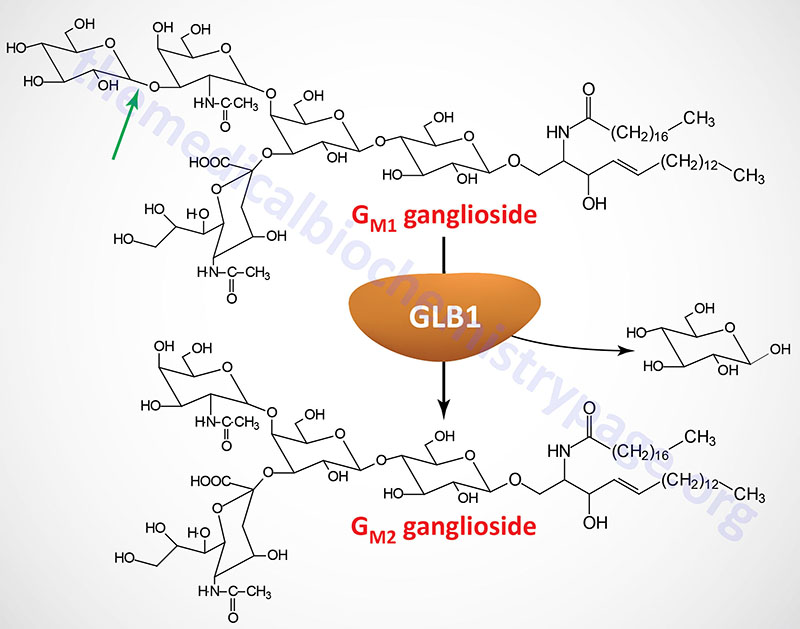
| GM1 Gangliosidosis | β-galactosidase (galactosidase beta 1) | GLB1 | also identified as a glycosphingolipid storage disease or lysosomal storage disease |
| Sandhoff disease | β-hexosaminidases A and B | HEXB | also identified as a glycosphingolipid storage disease or lysosomal storage disease |
| Sialidosis; type 1 (adult) and type 2 (infantile) | neuraminidase 1 (sialidase) | NEU1 | type 1 sialidosis is also known as cherry-red spot myoclonus syndrome; type 2 is also identified as mucolipidosis I (ML-I); neurominidase 1 requires the accessory protein: protective protein/cathepsin A (PPCA) which is encoded by the CTSA gene; type I associated with myoclonus, gait disturbances, reduced visual acuity with cherry-red macula; type II is associated hydrops fetalis, hepatosplenomegaly, dysostosis multiplex, coarse facial features, myoclonus, ataxia, tremor and angiokeratoma; see the Sialidosis page for details |
| Fucosidosis | α-L-fucosidase 1 | FUCA1 | two primary types: type 1 and type 2; type 1 is more severe and manifest in infancy; progressive motor and mental deterioration, growth impairment, coarse facial features, recurrent sinus and pulmonary infections |
| Schindler disease | α-N-acetylgalactosaminidase | NAGA | three subtypes: Type I (also known as infantile-onset neuroaxonal dystrophy); rapid psychomotor deterioration and seizures Type II (also known as Kanzaki disease); mild cognitive impairment, sensorineural hearing loss and angiokeratomas Type III (also known as intermediate severity); developmental delay, seizures, cardiomyopathy hepatomegaly |
Table of the Disorders Associated with Abnormal Sphingolipid Metabolism
| Disorder | Enzyme Deficiency | Gene | Accumulating Substance | Comments / Symptoms |
| Tay-Sachs disease | β-hexosaminidase A | HEXA | GM2 ganglioside | β-hexosaminidase A is a heterodimer composed of an α-subunit encoded by the HEXA gene and a β-subunit encoded by the HEXB gene; in the infantile form there is rapidly progressing psychomotor impairment, blindness, early mortality |
| Sandhoff disease | β-hexosaminidases A and B | HEXB | globoside; GM2 ganglioside | β-hexosaminidase A is a heterodimer of composed of an a-subunit encoded by the HEXA gene and a β-subunit encoded by the HEXB gene; β-hexosaminidase B is a homodimer of two β-subunits encoded by the HEXB gene; the infantile form manifests with the same symptoms as Tay-Sachs; disease progresses more rapidly than Tay-Sachs |
| Tay-Sachs AB variant GM2 activator deficiency | GM2 ganglioside activator | GM2A | GM2 ganglioside | the GM2 ganglioside activator protein is encoded by the GM2A gene; the infantile form manifests with the same symptoms as Tay-Sachs |
| Gaucher disease | glucocerebrosidase (glucosylceramidase beta) | GBA1 | glucocerebrosides | glucocerebrosidase is encoded by the glucosylceramidase beta (GBA) gene; most common form has average age of onset of 30 years; hallmark of disease is accumulation of lipid-engorged cells of the monocyte/macrophage lineage in multiple tissues |
| Fabry disease | α-galactosidase A | GLA | globotriaosylceramide; also called ceramide trihexoside (CTH) | kidney failure, skin rashes |
| Niemann-Pick diseases Types A and B | sphingomyelinase | SMPD1 | sphingomyelins | the sphingomyelinase that is defective in Niemann-Pick type A (NPA) and NPB is encoded by the SMPD1 (sphingomyelin phosphodiesterase 1) gene; humans express four genes with sphingomyelin phosphodiesterase activity (SMPD1, SMPD2, SMPD3, and SMPD4; type A is severe disorder with hepatosplenomegaly, severe neurological involvement leading to early death; type B is only associated with visceral involvement |
| Niemann-Pick disease Type C | NPC1 protein | NPC1 | LDL-derived cholesterol | cholesterol, sphingolipids, and other lipids accumulate in the late endosomes/lysosomes (LE/L) of all cells; characteristic phenotypes associated with “classic” NPC1 disease are variable hepatosplenomegaly, progressive ataxia, dystonia, dementia and vertical supranuclear gaze palsy (VSGP) |
| Krabbe disease; globoid cell leukodystrophy (GLD) | galactocerebrosidase | GALC | galactocerebrosides | galactocerebrosidase is encoded by the GALC (galactosylceramidase) gene; intellectual impairment, myelin deficiency |
| GM1 gangliosidosis | β-galactosidase-1 | GLB1 | GM1 gangliosides | β-galacatosidase-1 is encoded by the GLB1 (galactosidase beta 1) gene; intellectual impairment, skeletal abnormalities, hepatomegaly |
| Metachromatic leukodystrophy; sulfatide lipodosis | arylsulfatase A | ARSA | sulfatides | arylsulfatase A is encoded by the ARSA gene; intellectual impairment, metachromasia of nerves |
| Farber lipogranulomatosis | acid ceramidase | ASAH1 | ceramides | acid ceramidase is encoded by the ASAH1 (N-acylsphingosine amidohydrolase 1) gene; hepatosplenomegaly, painful swollen joints |
| Sialidosis; type 1 (adult) and type 2 (infantile) | neuraminidase 1 (sialidase) | NEU1 | sialyloligosaccharides in glycolipids and glycoproteins | type 1 sialidosis is also known as cherry-red spot myoclonus syndrome; type 2 is also identified as mucolipidosis I (ML-I); neurominidase 1 requires the accessory protein: protective protein/cathepsin A (PPCA) which is encoded by the CTSA gene; type I associated with myoclonus, gait disturbances, reduced visual acuity with cherry-red macula; type II is associated hydrops fetalis, hepatosplenomegaly, dysostosis multiplex, coarse facial features, myoclonus, ataxia, tremor and angiokeratoma; see the Sialidosis page for details |
Table of Disorders of Sialic Acid Metabolism
| Disease | Enzyme Deficiency | Gene | Symptoms / Comments |
| Galactosialidosis | neuraminidase 1 and β-galactosidase | CTSA | also identified Goldberg syndrome; disorder can also be the result of a secondary deficiency in β-galactosidase and neuraminidase-1; three distinct subtypes: early infantile, late infantile, and juvenile or adult; see the Galactosialidosis page for details |
| Infantile free sialic acid storage disease (ISSD) | sialin | SLC17A5 | most severe form of free sialic acid storage disorders (FSASD) which includes the intermediate severe and Salla form of disease resulting from mutations in the SLC17A5 gene; symptoms often evident before birth which is intrauterine hydrops; severe developmental delays, hypotonia, coarse facial features, seizures, and an enlarged liver, spleen, and heart (hepatosplenomegaly and cardiomegaly) |
| Intermediate severe Salla disease | sialin | SLC17A5 | less severe form of ISSD but more severe than Salla disease; manifest in first six months of life; symptoms include severe hypotonia, developmental delay, and possible seizures; most often due to inheritance of the most common allele found in Salla disease and one addition mutant SLC17A5 allele |
| Salla disease | sialin | SLC17A5 | less severe form of ISSD; symptoms include gradual loss of muscle tone associated with ataxia, intellectual disability, seizures, athetosis (involuntary movements), and spasticity; most commonly identified mutation Arg 39 mutation to Cys (R39C) |
| Sialuria | glucosamine (UDP-N-acetyl)-2-epimerase/N-acetylmannosamine kinase | GNE | developmental delay, hepatosplenomegaly, coarse facial features, seizures, joint pain, and recurrent infections |
Table of Lipid Storage Disorders
| Disease | Enzyme Deficiency | Gene | Symptoms / Comments |
| Acid lipase deficiency | lysosomal acid lipase | LIPA | also referred to as Wolman disease or cholesterol ester storage disease (CESD); LIPA encoded enzyme is also referred to as cholesterol ester hydrolase; Wolman disease is severe form of LIPA deficiency (no enzyme activity), CESD mild form (some residual enzyme activity); Wolman disease associated with massive infiltration of organs with macrophages filled with triglycerides and cholesteryl esters, death occurs early in life; CESD is slowly progressing disease that primarily affects the liver |
| Multiple sulfatase deficiency | sulfatase modifying factor 1 | SUMF1 | SUMF1 encoded enzyme is also known as formylglycine-generating enzyme (FGE); the enzyme catalyzes the hydrolysis of sulfate esters by oxidizing a target cysteine residue in substrate sulfatases, this oxidation creates an active site 3-oxoalanine residue (also known as a C-alpha-formylglycine residue); there are three forms: infantile, late infantile, and juvenile; the infantile form is associated with seizures, severe psychomotor retardation, coarse facial features, and hepatosplenomegaly; the late infantile form is associated with initial normal development followed by a plateau and then regression, symptoms include ichthyosis, dysostosis multiplex and coarse facial features; the juvenile form is associated with psychomotor regression over a prolonged period following typical development until middle to late childhood |
| I-Cell disease also called mucolipidosis IIA (ML-IIA) or mucolipidosis IIalpha/beta (ML-IIα/β) | UDP-N-acetylglucosamine:lysosomal-enzyme N-acetylglucosaminyl-1-phosphotransferase α- and β-subunits commonly called: GlcNAc-phosphotransferase | GNPTAB | the GNPTAB gene encodes both the α- and β-subunits of the hexameric (α2β2γ2) enzyme; the γ-subunit is encoded by the GNPTG gene; coarse facial features, gingival hypertrophy, recurrent otitis media, cardiac valvular disease; see the I-Cell Disease page for details |
| Pseudo-Hurler polydystrophy also called mucolipidosis III α/β, ML-IIIα/β | UDP-N-acetylglucosamine:lysosomal-enzyme N-acetylglucosaminyl-1-phosphotransferase α- and β-subunits commonly called: GlcNAc-phosphotransferase | GNPTAB | the GNPTAB gene encodes both the α- and β-subunits of the hexameric (α2β2γ2) enzyme; the γ-subunit is encoded by the GNPTG gene; less severe than I-cell disease; short stature, dysostosis multiplex, joint contractures, thickened skin; see the Pseudo-Hurler polydystrophy page for details |
| Mucolipidosis IIIγ (variant pseudo-Hurler polydystrophy) | UDP-N-acetylglucosamine:lysosomal-enzyme N-acetylglucosaminyl-1-phosphotransferase γ-subunit commonly called: GlcNAc-phosphotransferase | GNPTG | the GNPTG gene encodes γ-subunit of the hexameric (α2β2γ2) enzyme; the α- and β-subunits are encoded by the GNPTAB gene; symptoms includes short stature, aortic valve abnormalities, dysostosis multiplex and normal to near-normal intelligence; see the Pseudo-Hurler polydystrophy page for details |
Table of Disorders Associated with Integral Membrane Enzymes
| Disease | Enzyme Deficiency | Gene | Symptoms / Comments |
| Cystinosis | cystinosin | CTNS | cystinosin is a lysosome-localized transporter for the efflux of cystine to the cytosol; three classified forms of cystinosis: infantile (nephropathic) form, juvenile (intermediate and late-onset) form, and adult (benign, ocular, and non-nephropathic) form; infantile form is the most common, representing nearly 95% of all identified cases and is associated with end-stage renal disease between the ages of 10 to 12; see the Cystinuria page for more details |
| Infantile sialic acid storage disease (ISSD) | sialin | SLC17A5 | sialin is a lysosome-localized transporter for the efflux of sialic acid to the cytosol; severe developmental delays, hypotonia, coarse facial features, seizures, and an enlarged liver, spleen, and heart (hepatosplenomegaly and cardiomegaly) |
| Danon disease | lysosomal associated membrane protein 2 | LAMP2 | LAMP2 protein involved in the process of autophagosome fusion with lysosomes; also protects lysosomal membranes from the activity of lysosomal hydrolases; pathologies include cardiomyopathy, cardiac arrhythmia, myopathy, intellectual disability with males more severely affected than females, and cardiac arrhythmia |
| Niemann-Pick disease type C1 and type C2 | NPC intracellular cholesterol transporter 1 NPC intracellular cholesterol transporter 2 | NPC1 NPC2 | NPC1 protein is an integral membrane protein primarily associated with intraluminal vesicles and multi-vesicular late endosomes; NPC2 protein localized to lumen of lysosomes; clinical phenotypes of NPC1 disease are sub-divided into five presentation classifications: perinatal, early infantile, late infantile, juvenile and adult; symptoms result as a consequence of errors in the trafficking of exogenous cholesterol; NPC1 pathology is characterized by the presence of lipid-laden foam cells in the visceral organs and the nervous system; hepatosplenomegaly, progressive ataxia, dystonia, dementia and vertical supranuclear gaze palsy (VSGP); death will ensue by the second or third decade |
| Mucolipidosis IV | mucolipin TRP cation channel 1 | MCOLN1 | receptors of the transient receptor potential (TRP) family of ion channels that represent a unique family of channel proteins that serve as cellular sensors for a wide array of both physical and chemical stimuli; the TRPM family is referred to as the mucolipin family which consists of three genes; also known as sialolipidosis and also as ganglioside sialidase deficiency; psychomotor delay, intellectual disability, hypotonia, spasticity, corneal clouding, retinopathy, achlorhydria (absence of hydrochloric acid in the gastric secretions), and iron deficiency anemia |
| Action myoclonus-renal failure syndrome (AMRF) | scavenger receptor class B member 2 | SCARB2 | protein localized to lysosomal and endosomal membranes; AMRF is also known as autosomal recessive progressive myoclonic epilepsy-4 (EPM4); adult-onset disorder associated with tremors, action myoclonus (disabling, involuntary, and rapid muscle jerking that is triggered by voluntary movement or the intention to move, hence the term “action”), peripheral neuropathy, sensorineural hearing loss, and proteinuria |
Table of Neuronal Ceroid Lipofuscinoses
The neuronal ceroid lipofuscinoses are also referred to as the cerebral neurofuscinoses and also as the ceroid-lipofuscinoses neuronal and as such are designated by the CLN acronym. These disorders get their name from the neuronal accumulation of the histopathologically recognizable lipid accumulations referred to as lipofuscin. Lipofuscin is pronounced: lip-oh-FYOO-shun. Lipofuscin is a yellowish lysosomal accumulation of proteins and lipids that serves as a biomarker for oxidative stress and cellular dysfunction.
| Disorder | Enzyme Deficiency | Gene | Comments / Symptoms |
| CLN1 | palmitoyl-protein thioesterase 1 | PPT1 | PPT1 encoded enzyme is a lysosomal hydrolase involved in the depalmitoylation of proteins; CLN1 is also known as Haltia–Santavuori disease and Infantile Neuronal Ceroid Lipofuscinosis (INCL); three clinical variants: infantile, juvenile, and adult; infantile form associated with developmental regression beginning around 18 months, hypotonia, cerebral atrophy, myoclonus, epilepsy, and vision loss; juvenile form associated with decline in intellectual progression in childhood, myoclonus, epilepsy, and vision loss; adult form is associated with Parkinsonian tremors and ataxia |
| CLN2 | tripeptidyl peptidase 1 | TPP1 | TPP1 encoded enzyme is a lysosomal peptidase that removes tripeptides from the N-terminus of target proteins; CLN2 is also known as Jansky–Bielschowsky disease; late infantile form and juvenile forms; late juvenile form associated with myoclonus, ataxia, and intractable epilepsy; the juvenile form is associated with severe ataxia but the developmental decline and myoclonus are milder than in the late infantile form |
| CLN3 | CLN3 lysosomal/endosomal transmembrane protein, battenin | CLN3 | battenin is a lysosomal membrane protein involved in trafficking of molecules between organelles, is also involved in regulation of lysosomal pH, and the regulation of synaptic transmission in the amygdala, hippocampus, and cerebellum; CLN3 is also known as Batten–Spielmeyer–Sjogren disease; symptoms include developmental regression, progressive visual loss, hypokinesia including muscle rigidity and slow or diminished movements |
| CLN4 | DnaJ heat shock protein family (Hsp40) member C5 | DNAJC5 | the DNAJC5 encoded protein functions as a co-chaperone in the misfolding-associated protein secretion (MAPS) pathway; also provides instructions for making a protein called cysteine string protein alpha (CSPα) which is associated with nerve cells in the brain; CLN4 is also known as Parry disease and Kufs type A and type B; symptoms of the Kufs type A form include progressive myoclonus epilepsy (PME), progressive epilepsy, dementia, and ataxia; symptoms of the Kufs type B form include behavioral changes, dementia, and facial dyskinesia |
| CLN5 | CLN5 lysosomal BMP synthase | CLN5 | the CLN5 encoded enzyme catalyzes the formation of bis(monoacylglycero)phosphate (BMP) from other lipids, a process crucial lysosomal function, cholesterol homeostasis, and lipid metabolism; symptoms include vision loss, regression of developmental milestones, myoclonic epilepsy, and ataxia |
| CLN6 | CLN6 transmembrane ER protein | CLN6 | the CLN6 encoded protein functions along with the CLN8 encoded protein as part of the EGRESS (ER-to-Golgi relaying of enzymes of the lysosomal system) complex to ensure lysosomal enzymes get to the lysosomes; there are two forms, juvenile and adult; the juvenile form is associated with vision loss, regression of developmental milestones, epilepsy, ataxia, myoclonus, and dysarthria (difficulty speaking clearly); the adult form is associated with ataxia, epilepsy, dysarthria, and progressive loss of intellectual function but is not accompanied by vision loss |
| CLN7 | major facilitator superfamily domain containing 8 | MFSD8 | the MFSD8 encoded protein is likely to be a lysosomal membrane transporter but as yet the molecules transported have not been characterized; onset of symptoms is late infantile to juvenile and includes vision loss, developmental regression, myoclonus, epilepsy, and ataxia |
| CLN8 | CLN8 transmembrane ER and ERGIC protein | CLN8 | the CLN8 encoded protein functions along with the CLN6 encoded protein as part of the EGRESS (ER-to-Golgi relaying of enzymes of the lysosomal system) complex to ensure lysosomal enzymes get to the lysosomes; the ERGIC acronym stands for endoplasmic reticulum (ER)–Golgi intermediate compartment; there are two forms, late infantile and juvenile; the late infantile form is associated with developmental delay, progressive myoclonus, seizures, and vision loss; the juvenile form is associated with intractable epilepsy with progressive decline |
| CLN9 | N/A | N/A | this classification is no longer used; clinically identical to CLN3 but faster progression |
| CLN10 | cathepsin D | CTSD | CTSD encoded protein is a lysosomal protease and activator of other lysosomal enzymes; two forms, congenital and late infantile; the congenital form is associated with microcephaly, neonatal epilepsy, respiratory insufficiency, and rigidity; the late infantile form, which may manifest in juveniles or adults, is associated with ataxia, cognitive decline, and vision loss |
| CLN11 | granulin precursor | GRN | the GRN encoded protein, termed progranulin, is processed to granulin; precise function of granulin has yet to be determined; disorder is associated with progressive loss of vision, seizures, cerebellar ataxia, and atrophy |
| CLN12 | ATPase cation transporting 13A2 | ATP13A2 | the ATP13A2 encoded protein is a lysosomal polyamine efflux transporter whose function prevents the accumulation of polyamines in the lysosome; CLN12 is also known as Kufor–Rakeb syndrome or PARK9; symptoms include akinesia, rigidity, dysarthria, and mood disturbances |
| CLN13 | cathepsin F | CTSF | CTSF encoded protein is a lysosomal protease; symptoms are adult in onset and include behavioral abnormalities and dementia |
| CLN14 | potassium channel tetramerization domain containing 7 | KCTD7 | the KCTD7 encoded protein functions as an adaptor in ubiquitin ligase complexes and functions to regulate neuronal cell excitability by hyperpolarizing the membrane; protein function is important in the process of autophagy; symptoms are infantile in onset and include developmental regression and progressive myoclonic epilepsy (PME) |