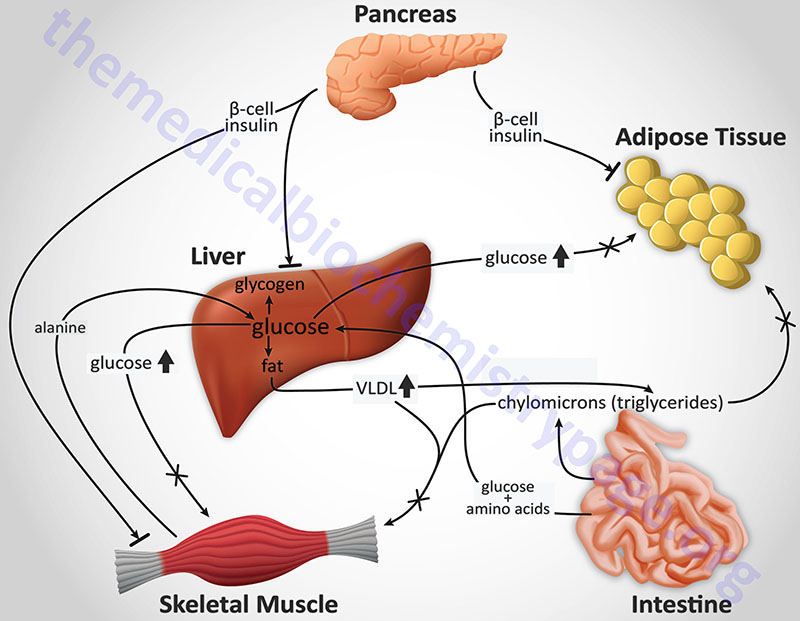
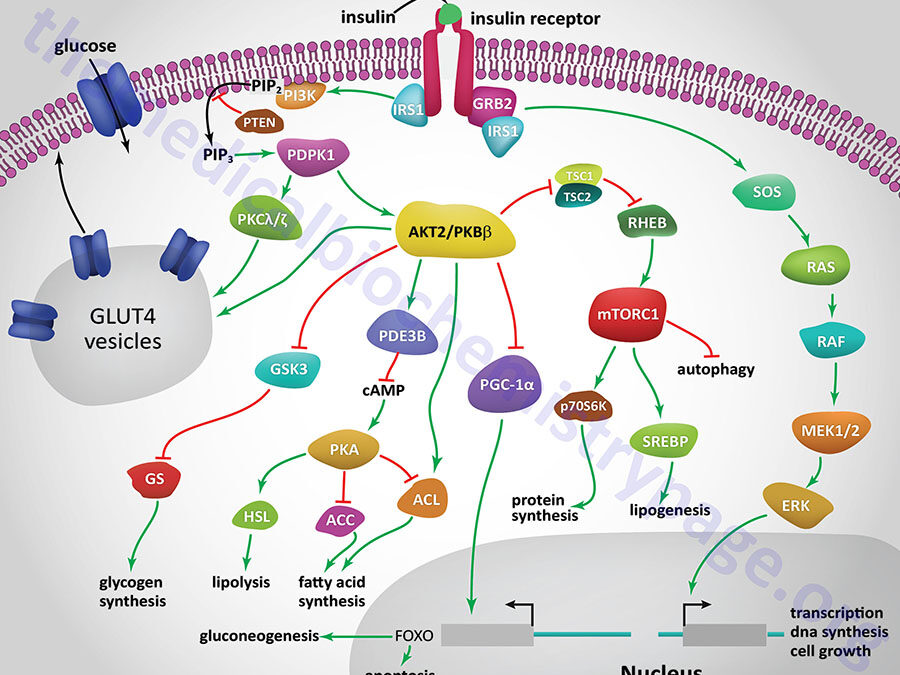
Last Updated: January 31, 2026 Definition of Diabetes Diabetes is any disorder characterized by excessive urine excretion. The most common form of diabetes is diabetes mellitus, a metabolic disorder in which there is an inability to maintain carbohydrate and lipid...