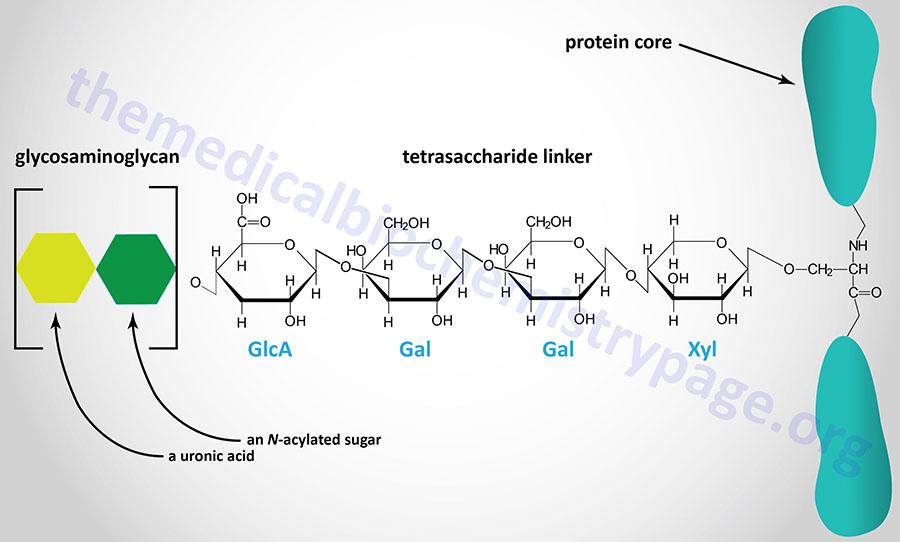
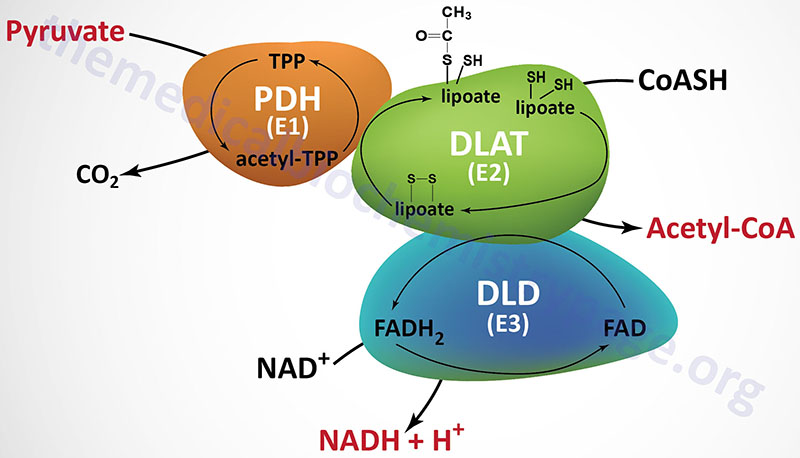
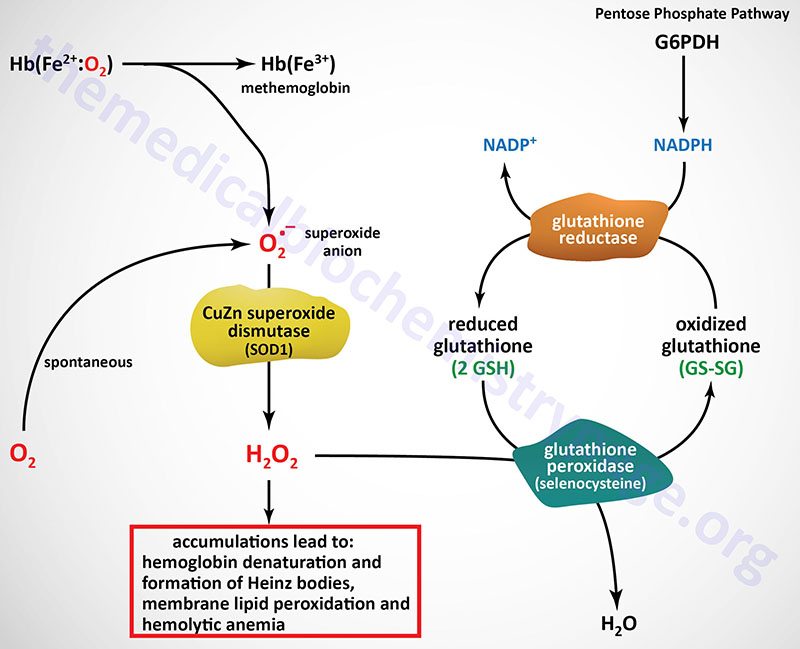
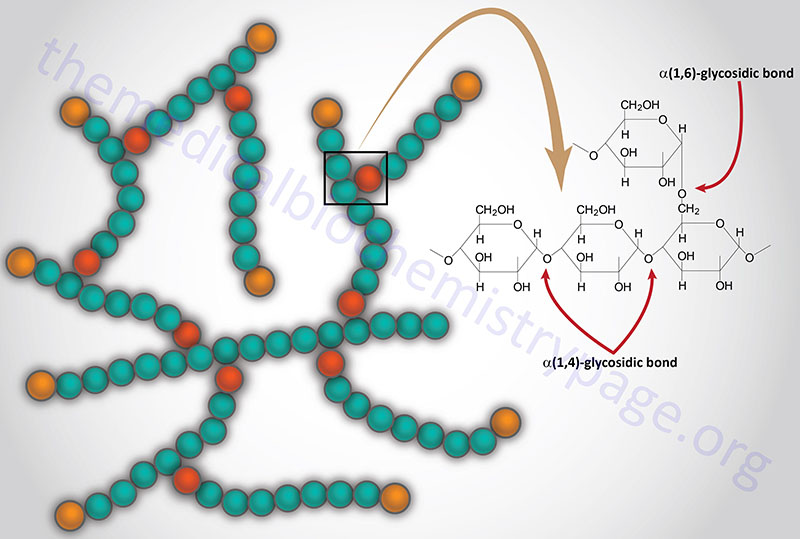
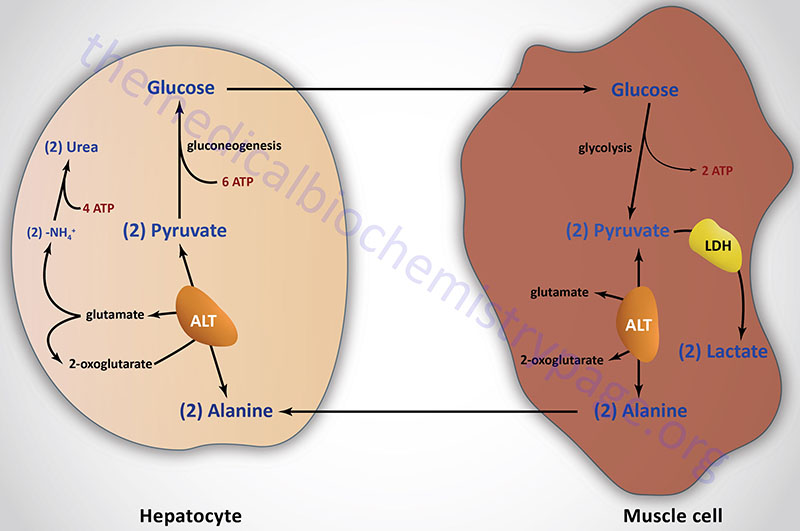
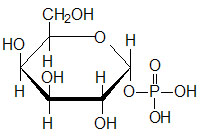
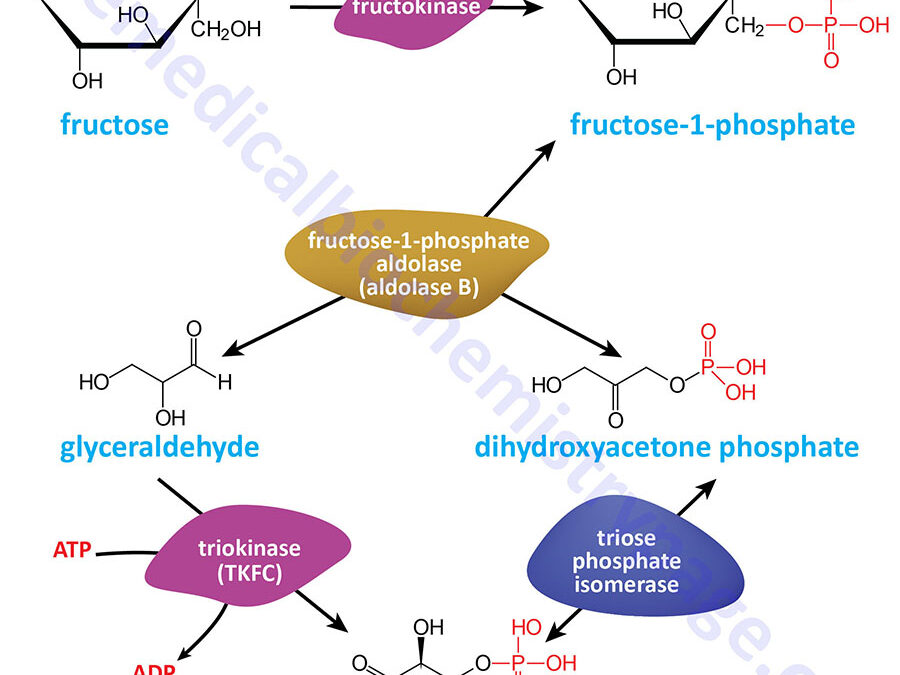
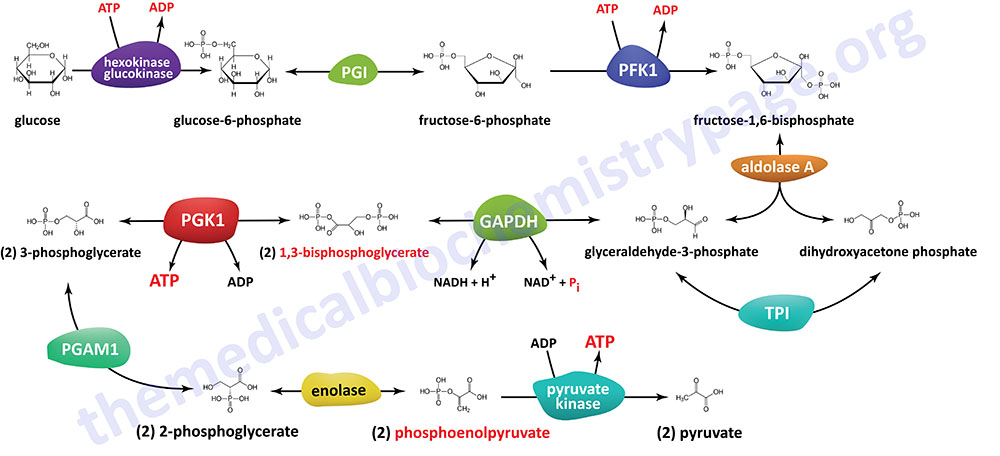
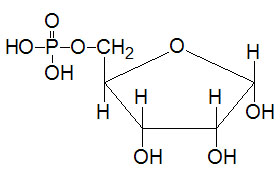
Last Updated: February 23, 2026 Glycosaminoglycans The most abundant heteropolysaccharides in the body are the glycosaminoglycans (GAGs). The glycosaminoglycans are historically referred to as the mucopolysaccharides given that they were originally characterized in...